Commonly Used Chinese Herb Formulas with Illustrations - Dang Gui and Bupleurum Formula (Xiao Yao San)
1120 逍遙散 (Xiao Yao San)
Dang Gui and Bupleurum Formula
Rambling Powder
【Formulation】
|
Chinese Name |
Pharmaceutical Name |
Pin Yin Name |
English Name |
|
白芍 |
Radix Paeoniae alba |
Bai Shao |
|
|
當歸 |
Radix Angelicae sinensis |
Dang Gui |
|
|
茯苓 |
Poria |
Fu Ling |
|
|
白朮 |
Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae |
Bai Zhu |
|
|
柴胡 |
Radix Bupleuri |
Chai Hu |
|
|
煨薑 |
Rhizoma Zingiberis preparata |
Wei Jiang |
|
|
炙甘草 |
Radix Glycyrrhizae praeparata cum melle |
Zhi Gan Cao |
|
|
薄菏 |
Herba Menthae |
Bo He |
【Classic Literature Reference】
Tai Ping Hui Min He Ji Ju Fang (Formulas of the Bureau of the People's Welfare Pharmacy, 1078).
Compiler: Chen, Shi-wen et al.
【Indications】
Traditional: Liver qi stagnation with blood deficiency marked by hypochondriac pain, alternating chills and fever, headache, blurred vision, dry mouth and throat, lassitude, reduced appetite, irregular menstruation, breast distention, a thin, white tongue coating, and a wiry and deficient pulse.
Modern: PMS, menopausal syndrome, leukorrhea, hyperplasia of mammary glands, dysmenorrhea, irregular menstruation, ovarian cyst, functional uterine bleeding, fibrocystic breasts, hyperplasia of mammary glands, pelvic inflammatory disease, depression, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, cholecystitis, pleurisy, chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, anemia, senile paralysis agitans, central retinitis, hyperlipidemia, and affective psychosis.1-3
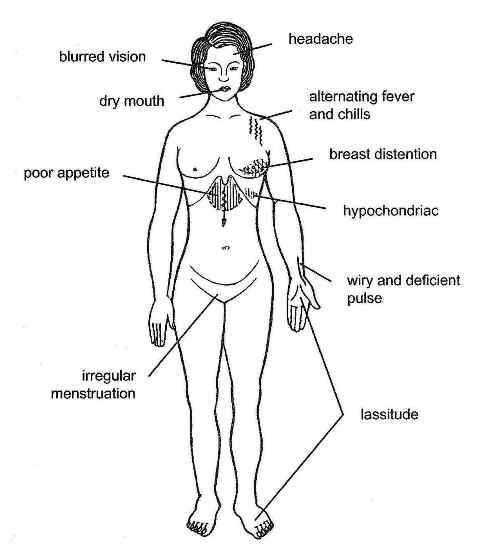
Pattern of Liver Qi Stagnation with Blood Deficiency
【Herbs and Actions】

Join our member to get full-text article! Join Free!
【Pharmacological Studies】for members only
【Clinical Applicaions】for members only
【Precaution & Contraindicaton】for members only
【Toxicity】for members only
【Discriminations】for members only
【References】for members only